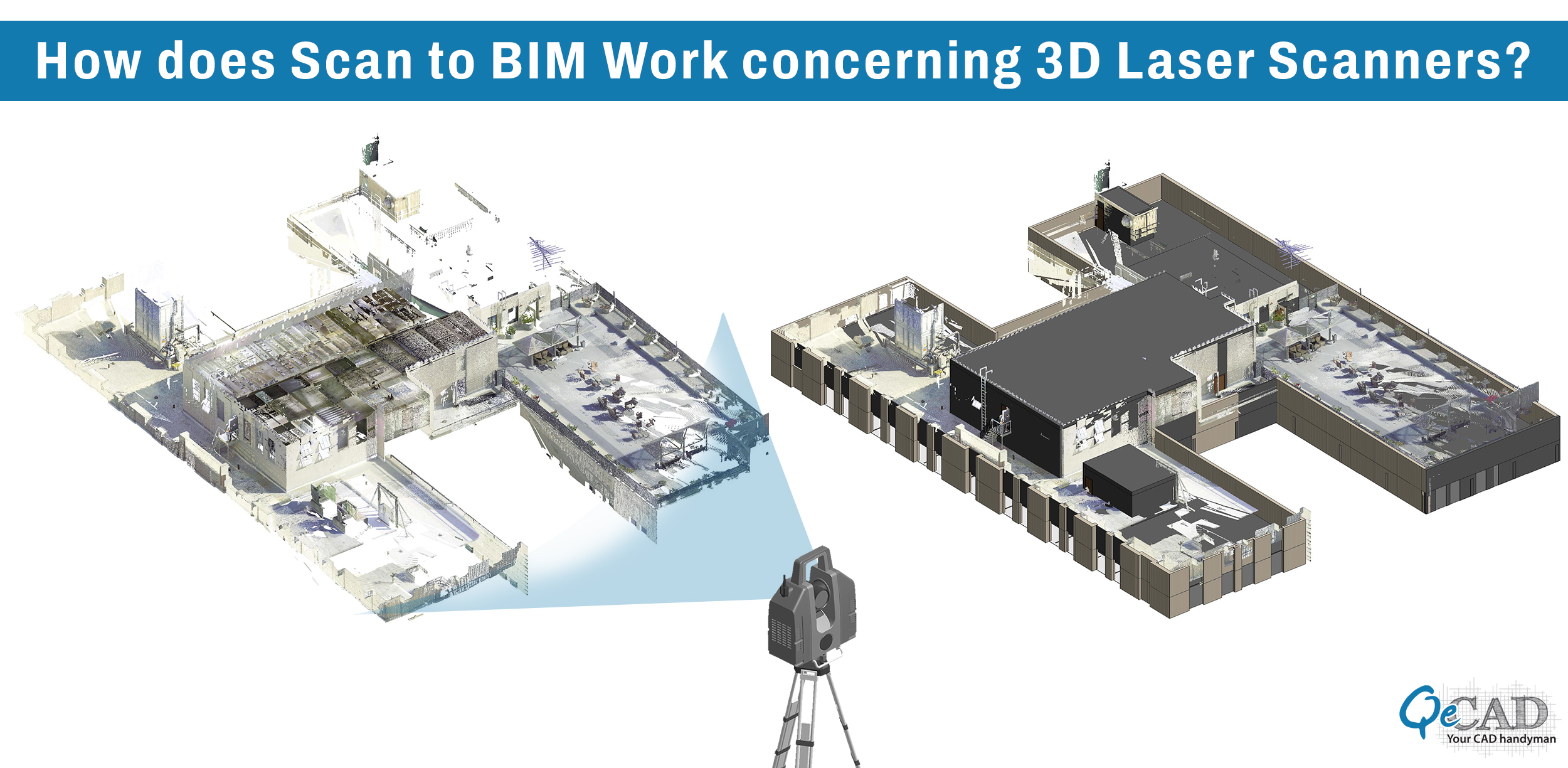
The penetration of Laser scanning technology in the AEC industry is proliferating. According to the sources, the laser scanning market is expected to reach USD 1324 million by 2026 from USD 924 million in 2021. The CAGR of laser scanning services is expected to increase by 7.5% within the tenure of 2021 to 2026. This continual boost of laser scanning technology would take the construction sector to the next level, facilitating the AEC professionals in the construction process of renovations, refurbishments, and retrofitting through Scan to BIM.
What exactly is Scan-to-BIM?
Scan to BIM, often termed Point Cloud Modelling, is a methodology of digitally representing the existing condition of any structure along with its physical and functional attributes via the 3D BIM Model. A laser scanner is used to capture accurate 3D scan data in the form of point clouds of any building structure, which then, with the help of 3D BIM software, is converted to As-built models to depict the designs in the actual context.
Scan-to-BIM services are helpful for projects relevant to restoration, retrofitting, and refurbishments. It helps in grabbing reliable and accurate information that can be used during construction. It enables data-rich and constructible workflow with the accuracy of measurements fetched from 3D laser scanners. Architects, engineers, and general contractors use laser Scan to BIM techniques for evaluation of the existing site, easy procurement, operations, and facility management, as well as assessing the energy efficiency aspects of the structure.
Workflow of Scan to BIM Conversion Process
The whole Scan to BIM process consists of the below significant stages.
1) Identifying the Requirements
The first and foremost step is to encapsulate the data, i.e., gather all the information relevant to 3D BIM modeling. This includes:
- Defining and documenting the actual scope of work
- Identifying the level of detail (LOD 100- LOD 500) required
- Defining required building elements
- Defining geometric and non-geometric attributes
- Defining required deliverable formats
- Determining the Tolerance level, etc.
2) Scan Planning
Under Scan Planning, the parameters or the attributes are determined beforehand, as this may prove beneficial before performing a 3D scan. This includes:
- Level of Accuracy
- Selecting the appropriate device
- Evaluating the space and angular Resolutions
- Selecting the proper location, etc.
3) Actual Scanning
Here, the actual scanning is performed, i.e., capturing the fundamental data with the help of a Laser Scanner like LiDAR. This scanning device has a laser rotating at high speed, and when the laser beam hits any surface, its position is recorded as coordinates (x, y, z) termed “points.” The collection of such points is mapped together, depicting the actual digital picture of the site from multiple views, termed a point cloud scan.
This point cloud scanning process can be performed using techniques such as 360 Degree scans, Time of Flight Scans, and Phase-based Scans using varied scanning tools like Faro, Trimble, Leica, etc.
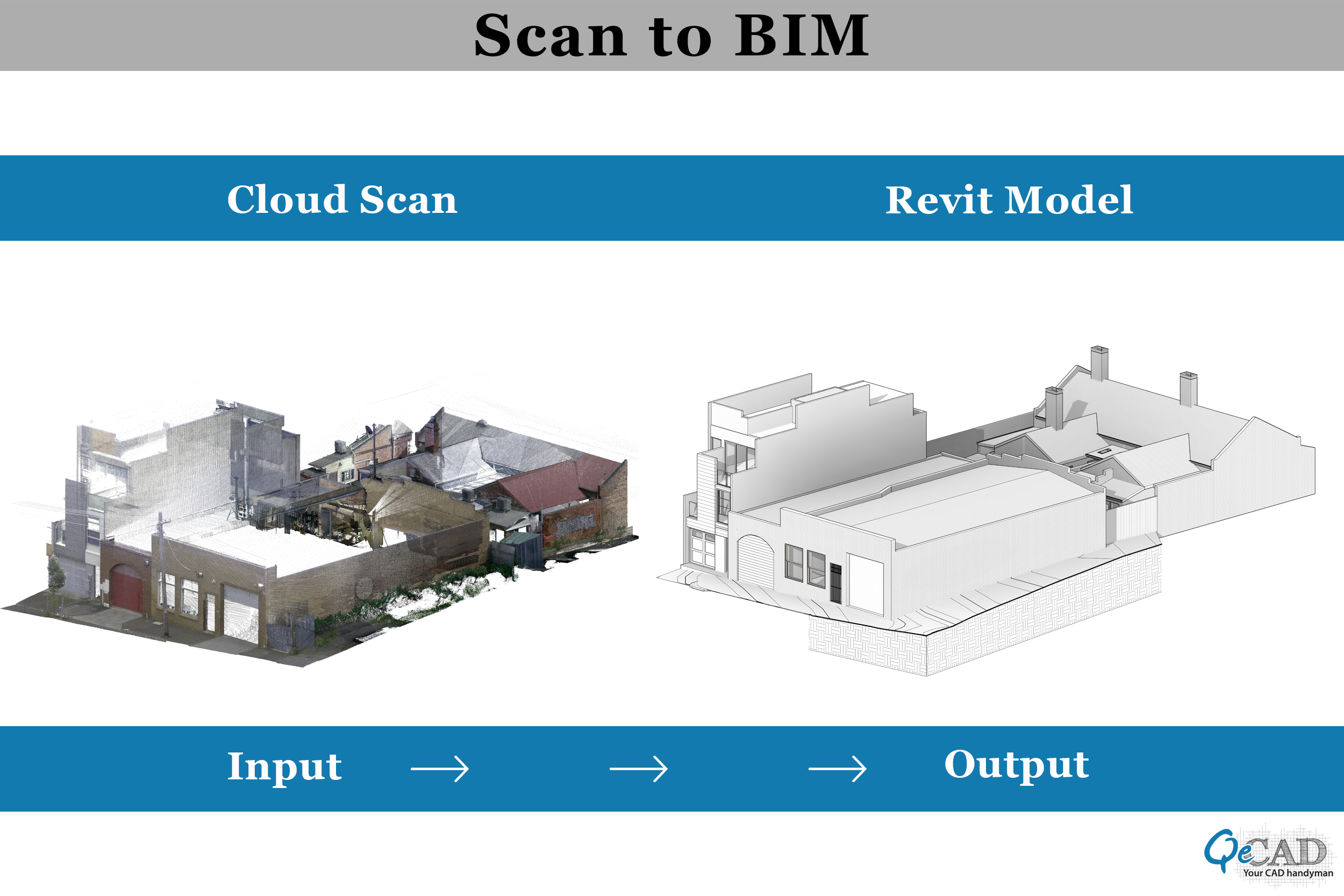 4) 3D Modeling
4) 3D Modeling
Once we get the point cloud scan of the structure, it is then registered and imported into a scanning software like Autodesk’s Recap to extract the relevant information about the structure, which the AEC professionals can use in numerous ways. This is termed Deciphering the point cloud data. The information includes:
- Point cloud scan file format (.rcp, .rcs)
- Coordinates
- Grid, Level, and Model alignments
At this stage of the Scan to BIM process, we get our As-built model with the necessary information, which later can be used for remodeling, redesigning, and renovations.
5) Quality Control
Once we have our 3D model handy, the last stage of Scan to BIM is performed, which is to thoroughly check out the quality with the help of Revit plugins. This QA/QC step is to ensure below points:
- Clash Detection and Coordination
- All the quality standards check boxes are ticked
- Verify work sets
- Ensure the Density and clarity of the scan
- Audit file
Conclusion
Scan to BIM services and its applications are technologically driving the AEC industry. Technology like Laser scanning helps ease the process of fetching and understanding the structure while redeveloping a site. This process streamlines the operations, saves construction time, cuts down costs, and ensures clash-free quality BIM models.